
 X-ray of the left knee revealed an ossicle anterior to the tibial tuberosity.
X-ray of the left knee revealed an ossicle anterior to the tibial tuberosity.
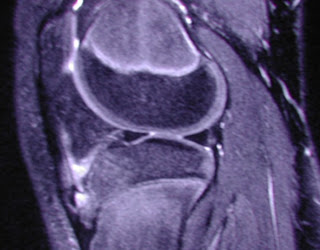
Diagnosis is most often made clinically. When used, radiography shows fragmentation of the tibial tubercle, although this finding alone may represent a normal ossification center. Therefore, the most important diagnostic criteria are seen at MR imaging and include:- soft-tissue swelling anterior to the tibial tuberosity, - loss of the sharp inferior angle of the infrapatellar fat pad and surrounding soft tissues,- thickening and edema of the inferior patellar tendon, and- infrapatellar bursitis.



No comments:
Post a Comment