1. Pulmonary edema
2. Pneumonia
3. Aspiration
4. Hemorrhage
this means presence of fluid inside alveoli which could be water as in pulmonary edema,exudate in pneumonia,blood in hemorrhage or any kind of aspiration materials.
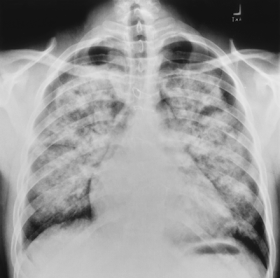
 1) Pulmonary Alveolar Edema. There is extensive, bilateral airspaces disease with fluid in the minor fissure (blue arrow) and bilateral pleural effusions (ref arrows). Although the heart is not enlarged, the cause was still on a cardiogenic basis.
1) Pulmonary Alveolar Edema. There is extensive, bilateral airspaces disease with fluid in the minor fissure (blue arrow) and bilateral pleural effusions (ref arrows). Although the heart is not enlarged, the cause was still on a cardiogenic basis.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.learningradiology.com/caseofweek/caseoftheweekpix2007-1/cow267arr.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.learningradiology.com/archives2007/COW%2520267-Pulmonary%2520edema-CHF/pulmedemacorrect.html&usg=__YRtgi0C8v73xQys3usyMs9_3_Vw=&h=443&w=500&sz=38&hl=en&start=8&sig2=GWET39uAxZAeo7LW_hF9VQ&itbs=1&tbnid=DIXYRi9W8kwI2M:&tbnh=115&tbnw=130&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dpulmonary%2Bedema%2Bx%2Bray%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=nHMwTNOmOMuTjAfIjbHDBQ
http://gardenrain.wordpress.com/2010/01/page/4/


No comments:
Post a Comment