Wednesday, March 30, 2011
ADC map differentiation between tumoral and non tumoral tissue
ADC MAP DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN TUMORAL AND NON TUMORAL TISSUE: -With high cellularity lesion , has a low ADC map value resulting in hypo intense signal. -While in low cellularity lesion such as edema , inflammation , fibrosis , and necrosis shows high ADC map signal.
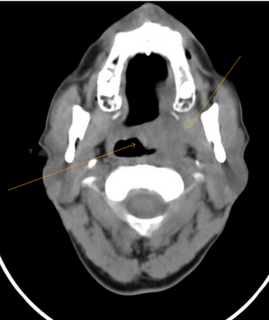 CT image of biopsy proven case of squamous cell carcinoma of left tonsil. http://sumerdoc.blogspot.com/2009/07/carcinoma-tonsil-ct.html
CT image of biopsy proven case of squamous cell carcinoma of left tonsil. http://sumerdoc.blogspot.com/2009/07/carcinoma-tonsil-ct.html Thursday, February 24, 2011
Hemangioma
Vertebral body hemangiomas are the most common tumors of the spinal axis and in most circumstances are incidental findings. Most hemangiomas are diagnosed based on their characteristic imaging findings, though the diagnosis can be challenging in cases of atypical or aggressive hemangiomas. In such cases, the recognition of vertically oriented coarse bony trabeculae surrounded by fatty stroma, resulting in the "salt and pepper" appearance on axial images and a striated appearance on coronal or sagittal images, is the key to the correct diagnosis. Though rare, aggressive hemangiomas can be symptomatic and pathologic fractures can lead to myelopathy and cord compression. In such patients, MR accurately displays the extraosseous extension of the hemangioma and its effect upon the spinal canal and cord.
Atypical hemangioma
 The T1-weighted sagittal image demonstrates an atypical hemangioma within the L1 vertebral body (arrow) with coarse trabeculae, but with relatively little typical fat signal within the lesion.
The T1-weighted sagittal image demonstrates an atypical hemangioma within the L1 vertebral body (arrow) with coarse trabeculae, but with relatively little typical fat signal within the lesion.Typical hemangioma
 The T2-weighted sagittal image shows a lesion of increased signal intensity replacing the entire L2 vertebral body. Coarse vertically oriented trabeculae are present (arrows).
The T2-weighted sagittal image shows a lesion of increased signal intensity replacing the entire L2 vertebral body. Coarse vertically oriented trabeculae are present (arrows). The T1-weighted sagittal image reveals that the L2 vertebral body lesion (arrow) is of increased signal intensity, similar to that seen on the T2-weighted image.
The T1-weighted sagittal image reveals that the L2 vertebral body lesion (arrow) is of increased signal intensity, similar to that seen on the T2-weighted image. The T1-weighted axial image demonstrates the coarse trabeculae on end surrounded by fat signal, resulting in a 'salt and pepper" appearance (arrow).
The T1-weighted axial image demonstrates the coarse trabeculae on end surrounded by fat signal, resulting in a 'salt and pepper" appearance (arrow).On plain radiographs, hemangiomas often have a vertically striated appearance due to thickening of bony trabeculae. This appearance has been described as "corduroy cloth" or "jail bar" and the overall density of the vertebral body is decreased due to the presence of fatty marrow.
With CT, vertebral body hemangiomas have low attenuation interspersed with thickened bony trabeculae, causing a characteristic "salt and pepper" or "polka dot" appearance on axial images.
With MR imaging, the intralesional fat of the hemangioma causes increased signal intensity on T1 weighted MR images.4 On T2-weighted images, the signal intensity of the hemangiomas also increases because of high water content,4 and the T2-hyperintensity is typically greater than that of fat, thereby differentiating hemangiomas from focal fat deposition.
These signal characteristics also differ from those of metastatic lesions, which have decreased signal intensity on T1 weighted images and increased signal intensity on T2 weighted images.
These signal characteristics also differ from those of metastatic lesions, which have decreased signal intensity on T1 weighted images and increased signal intensity on T2 weighted images.
Friday, February 4, 2011
Saturday, January 1, 2011
Finding Early Invasive Breast Cancers: A Practical approach
http://www.google.com.kw/imgres?imgurl=http://radiology.rsna.org/content/248/1/61/F12.large.jpg&imgrefurl=http://radiology.rsna.org/content/248/1/61/F12.expansion&usg=__eejoQeCsmxs9g-MAIkvhlm9IRPA=&h=1800&w=1639&sz=279&hl=ar&start=6&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=JSfMvlnSVujnoM:&tbnh=150&tbnw=137&prev=/images%3Fq%3Darchitecture%2Bdistortion,mammography%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1
please click on the above link,then go to right column under this article and click figure only.
please click on the above link,then go to right column under this article and click figure only.
Friday, December 24, 2010
inferior gleno-humeral ligament tear
 The corresponding axial view confirms the edematous inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow). Extracapsular fluid compatible with capsular disruption (arrowheads) is also noted.
The corresponding axial view confirms the edematous inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow). Extracapsular fluid compatible with capsular disruption (arrowheads) is also noted. The T2-weighted coronal oblique image reveals a lax and edematous inferior glenohumeral ligament, having a "J-shaped" appearance (arrows). The usual attachment of the ligament along the medial aspect of the proximal humerus (arrowhead) is not identified.
The T2-weighted coronal oblique image reveals a lax and edematous inferior glenohumeral ligament, having a "J-shaped" appearance (arrows). The usual attachment of the ligament along the medial aspect of the proximal humerus (arrowhead) is not identified.inferior gleno-humeral ligament tear
 Coronal MR arthrogram of left shoulder revealing avulsion of inferior glenohumeral ligament complex off of the humeral head. The arrow indicates the detached ligament from the humerus.
Coronal MR arthrogram of left shoulder revealing avulsion of inferior glenohumeral ligament complex off of the humeral head. The arrow indicates the detached ligament from the humerus.http://www.google.com.kw/imgres?imgurl=http://www.orthosupersite.com/images/content/obj/0808/ParameswaranF2.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.orthosupersite.com/view.aspx%3Frid%3D30521&usg=__tSIaEL-mzmXfUaNAPX5o7o1Swdg=&h=231&w=300&sz=12&hl=ar&start=7&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=3t3BTF93IM9hKM:&tbnh=89&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dglenohumeral%2Bligaments%2Btears%26hl%3Dar%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1
supra-spinatous tendon(anatomy)
 The image above is the patient’s pre-injection coronal MRI. The rotator cuff tendon is the area of interest. The rotator cuff is compromised of 4 principle muscles. Muscles have two parts: the muscle belly and the attachment of the muscle to bone(tendon). Tears in the rotator cuff commonly involve the tendon.
The image above is the patient’s pre-injection coronal MRI. The rotator cuff tendon is the area of interest. The rotator cuff is compromised of 4 principle muscles. Muscles have two parts: the muscle belly and the attachment of the muscle to bone(tendon). Tears in the rotator cuff commonly involve the tendon.supra-spinatous tendon tear (partial)
 47-year-old man with shoulder pain. Patient had surgically proven partial-thickness bursal surface supraspinatus tendon tear. Oblique coronal fast spin-echo fat-saturated T2-weighted (TR/TE, 3,850/55) MR image shows findings consistent with partial-thickness bursal surface supraspinatus tendon tear (arrow).
47-year-old man with shoulder pain. Patient had surgically proven partial-thickness bursal surface supraspinatus tendon tear. Oblique coronal fast spin-echo fat-saturated T2-weighted (TR/TE, 3,850/55) MR image shows findings consistent with partial-thickness bursal surface supraspinatus tendon tear (arrow).http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/full/187/4/881/FIG1
Friday, November 26, 2010
breast cyst
breast fibro-adenoma
 Ultrasonogram demonstrates a hypoechoic mass with smooth, partially lobulated margins typical of a fibroadenoma.
Ultrasonogram demonstrates a hypoechoic mass with smooth, partially lobulated margins typical of a fibroadenoma.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://img.medscape.com/pi/emed/ckb/radiology/336139-345779-1932.jpg&imgrefurl=http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/345779-overview&usg=__tO5wEe1ECJuuvpxvv0qEyd8rlkM=&h=400&w=432&sz=35&hl=ar&start=15&sig2=PrLsvJOjsA9_PHpveWNIXQ&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=oEbkYKbqzrktdM:&tbnh=117&tbnw=126&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbreast%2B,fibro%2Badenoma%26hl%3Dar%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=0h3wTOH6HoqUOvPmrfIJ
breast abscess
D.D. of spiculated breast mass
D.D. of spiculated breast mass
1- carcinoma.
2-radial scar.
3-fat necrosis.
1- carcinoma.
2-radial scar.
3-fat necrosis.
breast,hamartoma,us
 Ultrasonogram demonstrates a 3-cm lobulated circumscribed mass that is predominantly hypoechoic (arrows). Some of the fatty tissue within the lesion is hyperechoic (arrowheads), although this is not seen in all hamartomas.
Ultrasonogram demonstrates a 3-cm lobulated circumscribed mass that is predominantly hypoechoic (arrows). Some of the fatty tissue within the lesion is hyperechoic (arrowheads), although this is not seen in all hamartomas.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://download.imaging.consult.com/ic/images/S1933033207712752/gr5-midi.jpg&imgrefurl=http://imaging.consult.com/image/topic/dx/Breast%3Ftitle%3DHamartomas%2520(Breast)%26image%3Dfig5%26locator%3Dgr5%26pii%3DS1933-0332(07)71275-2&usg=__GGlXaFZXLVESuRAP_3Wa4GxZm5A=&h=200&w=194&sz=7&hl=ar&start=1&sig2=9YhcxLxWCD8_KyJ_4waZog&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=fIB9is-QR5OICM:&tbnh=104&tbnw=101&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbreast%2Bhamartoma,ultrasound%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=8ArwTNL-IsGEOtyjuYMK
breast fat necrosis
 Early fat necrosis in hematoma. This woman had suffered blunt trauma to the chest wall in an automobile accident 3 weeks before the mammogram. This 2-cm lobular circumscribed mass (arrows) contains both fat and soft-tissue density (blood). This completely resolved within 6 months of the trauma.
Early fat necrosis in hematoma. This woman had suffered blunt trauma to the chest wall in an automobile accident 3 weeks before the mammogram. This 2-cm lobular circumscribed mass (arrows) contains both fat and soft-tissue density (blood). This completely resolved within 6 months of the trauma.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://download.imaging.consult.com/ic/images/S1933033207712752/gr2-midi.jpg&imgrefurl=http://imaging.consult.com/imageSearch%3Fquery%3Dtissue%26qyType%3DAND%26global_search%3DSearch%26modality%3D%26thes%3Dtrue%26normalVariantImage%3Dfalse%26groupByNode%3Dnone%26anatomicRegion%3D%26modalityFilter%3DMammography&usg=__cPjcJ_19wJ8oniLC9qJup700eEg=&h=148&w=200&sz=3&hl=ar&start=7&sig2=ekkxOLMcJQb1q-rrKBAYJg&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=i4GCw-2kGvn_HM:&tbnh=77&tbnw=104&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbreast%2Bhamartoma,ultrasound%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=-gfwTMiPCcOcOqzipPoJ
breast amartoma
 A 3-cm oval circumscribed mass (arrows) containing both fat and soft-tissue density.
A 3-cm oval circumscribed mass (arrows) containing both fat and soft-tissue density.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://download.imaging.consult.com/ic/images/S1933033207712752/gr2-midi.jpg&imgrefurl=http://imaging.consult.com/imageSearch%3Fquery%3Dtissue%26qyType%3DAND%26global_search%3DSearch%26modality%3D%26thes%3Dtrue%26normalVariantImage%3Dfalse%26groupByNode%3Dnone%26anatomicRegion%3D%26modalityFilter%3DMammography&usg=__cPjcJ_19wJ8oniLC9qJup700eEg=&h=148&w=200&sz=3&hl=ar&start=7&sig2=ekkxOLMcJQb1q-rrKBAYJg&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=i4GCw-2kGvn_HM:&tbnh=77&tbnw=104&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbreast%2Bhamartoma,ultrasound%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=-gfwTMiPCcOcOqzipPoJ
breast,hamartoma
 At mammography, fibroadenolipoma are typically well-circumscribed, round to oval masses containing both fat and soft-tissue density with a thin, radiopaque pseudocapsule.
At mammography, fibroadenolipoma are typically well-circumscribed, round to oval masses containing both fat and soft-tissue density with a thin, radiopaque pseudocapsule.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.radswiki.net/main/images/thumb/7/79/Breast-hamartomas-002.jpg/97px-Breast-hamartomas-002.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.radswiki.net/main/index.php%3Ftitle%3DFibroadenolipoma&usg=__QmqZY5_p3AJ1HjJPraZkZ8CKrGE=&h=119&w=97&sz=2&hl=ar&start=3&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=qDniGsX3nGcSsM:&tbnh=88&tbnw=72&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbreast%2Bhamartoma%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1
Thursday, November 25, 2010
breast,lipoma
 The radiopaque capsule (arrowheads) is visible around all except the most posterior aspect of the mass.
The radiopaque capsule (arrowheads) is visible around all except the most posterior aspect of the mass.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://download.imaging.consult.com/ic/images/S1933033207712892/gr3-midi.jpg&imgrefurl=http://imaging.consult.com/image/topic/dx/Breast%3Ftitle%3DLipoma%2520(Breast)%26image%3Dfig3%26locator%3Dgr3%26pii%3DS1933-0332(07)71289-2&usg=__Xxezrq-JmuA9bY_ir4smb3EdGM4=&h=200&w=190&sz=4&hl=ar&start=1&sig2=NuP5-leUiMRhwNR-4ch6mg&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=LIjuQlk-s5spbM:&tbnh=104&tbnw=99&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dlipoma,breast%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=icbuTOPwL4iChQfMmYm5Cg
breast,galactocele
 A
A
B
Cystic mass with fat-fluid level galactocele. (a) Mammogram reveals an oval circumscribed mass with the characteristic fat-fluid level (arrows). In this type of galactocele, the milk content is fresh and fluid, allowing the fat to rise and the heavier water content to remain in the lower portion of the cyst. (b) US image also demonstrates the fat-fluid level (long arrows), with typical high and low echogenicity. Note that the fatty component has risen and occupies the upper (nondependent) portion of the cyst, whereas the heavier water content remains in the lower (dependent) portion. Note also the clot of fatty milk (“cream”) (short arrow) floating in the nondependent portion of the cyst owing to its intermediate density.
http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/27/suppl_1/S101.figures-only
breast,plasma cell mastitis
 Large Rod-like, Plasma cell mastitis
Large Rod-like, Plasma cell mastitishttp://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/images/thmb_47ebcfe54f241plasmacel-mastitis.png&imgrefurl=http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/4793bfde0ed53&usg=__J6Yl7bUKHxofKgE908rME1K03w8=&h=168&w=370&sz=56&hl=ar&start=4&sig2=AUHJw8vTzWTngE5vcWn2tQ&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=8G4pF9EmrBilRM:&tbnh=55&tbnw=122&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dplasma%2Bcell%2Bmastitis%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=lcLuTPPXJMqwhAf1wJirCg
breast,plasma cell mastitis
 Large rod shaped cacifications, multiple, sometimes branching and symetric in many cases. Note the dense, smooth, thick character that distinguishs these from the much softer, irregular, smaller calcifications of intraductal cancer.
Large rod shaped cacifications, multiple, sometimes branching and symetric in many cases. Note the dense, smooth, thick character that distinguishs these from the much softer, irregular, smaller calcifications of intraductal cancer.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://radiology.creighton.edu/basic/mmg/image170.gif&imgrefurl=http://radiology.creighton.edu/mammo.htm&usg=__NgNDvx5eHnmmlqiRuX-ou3-jODQ=&h=241&w=216&sz=5&hl=ar&start=3&sig2=kAhdkWXE4WaImzUxVWZ2oQ&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=Ml7WuSuICo7E4M:&tbnh=110&tbnw=99&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dplasma%2Bcell%2Bmastitis%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=TMHuTJ3aN4q3hQe8ssmoCg
breast,duct ectasia
 Duct ectasia in the right breast in a 13-year-old girl. US scan depicts anechoic tubular structures.
Duct ectasia in the right breast in a 13-year-old girl. US scan depicts anechoic tubular structures.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/20/6/1613/F22.large.jpg&imgrefurl=http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/20/6/1613/F22.expansion&usg=__N3ecBH95OaAq2b_NcwMQZrDhtOw=&h=1456&w=1800&sz=321&hl=ar&start=1&sig2=txBavFP3CTgnpLBEf23IZw&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=IgjqiXE3BF686M:&tbnh=121&tbnw=150&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dduct%2Bectasia,breast%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=2mbuTMDcK9GB4Qam6anHCg
breast,duct ectasia
 This magnification left mediolateral galactogram demonstrates diffuse mild dilatation of the ducts. There were no persistent filling defects.
This magnification left mediolateral galactogram demonstrates diffuse mild dilatation of the ducts. There were no persistent filling defects.http://www.google.com.eg/imgres?imgurl=http://download.imaging.consult.com/ic/images/S1933033207712806/gr8-midi.jpg&imgrefurl=http://imaging.consult.com/image/topic/dx/Breast%3Ftitle%3DDuct%2520Ectasia%2520(Breast)%26image%3Dfig8%26locator%3D%26pii%3DS1933-0332(07)71280-6&usg=__90pbK4AcnglA5j71K6x70UxHq1g=&h=185&w=200&sz=4&hl=ar&start=13&sig2=0kdrB08PCwl4rO0AciPj9Q&zoom=1&itbs=1&tbnid=bAQUJoHIlrduXM:&tbnh=96&tbnw=104&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dduct%2Bectasia,breast%26hl%3Dar%26sa%3DG%26gbv%3D2%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=AmbuTOzKB8SB4Qa5poWkCg
breast,papilloma
 A
A B
BImages of a 4-mm benign intraductal papilloma in a 46-year-old woman with recent onset of reproducible dark sanguinous discharge from the right nipple. The mammogram and US image (not shown) were unremarkable. (a) Craniocaudal digital galactogram obtained with the patient in a prone position shows a 4-mm rectangular filling defect (arrow) with a smaller round bubble (arrowhead) immediately inferior to it. (b) Paired craniocaudal stereotactic images show the filling defect (arrows) and bubble (arrowheads); targeting was performed by using these paired images.
http://radiology.rsna.org/content/218/2/576.figures-only
breast,intra-ductal papilloma
 Duplex Doppler images of the left subareolar region show that the intraluminal mass has arterial flow.
Duplex Doppler images of the left subareolar region show that the intraluminal mass has arterial flow.http://radiology.rsna.org/content/210/3/795.figures-only
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)














